VOLUME 5 NUMBER 1 (January to June 2012)
Philipp. Sci. Lett. 2012 5 (1) 090-102
available online: June 15, 2012
*Corresponding author
Email Address: nrojas@ateneo.edu.ph
Submitted: February 15, 2012
Revised: March 28, 2012
Accepted: April 01, 2012
ARTICLE
Partial gene sequence and characterization of EDEN-1, a major water-soluble protein from the economically important alga Eucheuma denticulatum
by Paulina B. Suarez-Aspilla1,2, Mailyn M. Terrado1, Maria Cristina A. Dancel3, Giuseppe C. Zuccarello4, Nina Rosario L. Rojas1,*
1Department of Chemistry, School of Science and Engineering, Ateneo de Manila
University, Loyola Heights, Quezon City, Philippines 1108
2Department of Chemistry, Silliman University, Dumaguete City, Philippines
3Mass Spectrometry Facility, Department of Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
32611- 7200, U. S. A.
4School of Biological Sciences, Victoria University of Wellington, PO Box 600, Wellington,
6140 New Zealand
University, Loyola Heights, Quezon City, Philippines 1108
2Department of Chemistry, Silliman University, Dumaguete City, Philippines
3Mass Spectrometry Facility, Department of Chemistry, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL
32611- 7200, U. S. A.
4School of Biological Sciences, Victoria University of Wellington, PO Box 600, Wellington,
6140 New Zealand
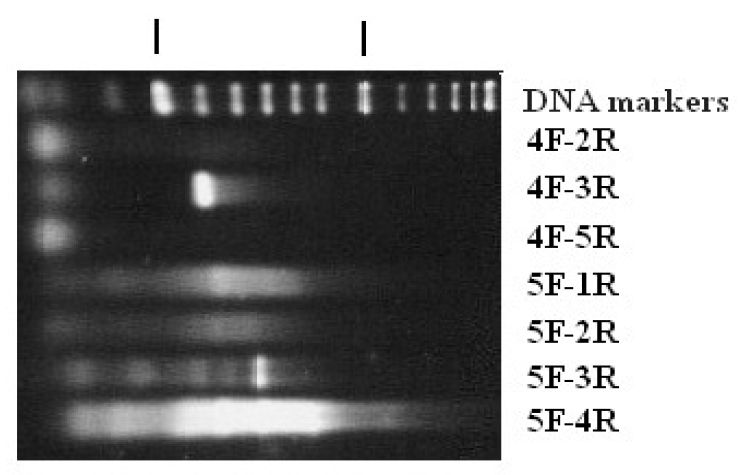
Eucheuma denticulatum is a major aquacultureproduct worldwide as a source for iota-carrageenan,but its protein chemistry is not well known.This study reports the isolation,characterization, and partial gene and amino acidsequences of a major water-soluble protein from E.denticulatum, which we called EDEN-1. The protein waspurified by ion-exchange chromatography on a strong anionexchanger. It is compact and monomeric by size exclusionchromatography, and has an intact molecular mass of 27.83 kDaby mass spectrometry. Its isoelectric point is 4.7, which isconsistent with its amino acid composition. It is notglycosylated, based on periodic acid-Schiff staining. Peptidesequencing by tandem mass spectrometry of tryptic fragmentsyielded 5 short internal peptide sequences. These peptidesequences were back-translated to design degenerate primers toobtain a partial cDNA sequence for EDEN-1. The results of denovo peptide sequencing and cDNA sequencing were combinedand verified with peptide mass fingerprinting of tryptic digests toyield partial gene and amino acid sequences of EDEN-1. Thissequence accounts for 13,414 Da, or 48.2% of the intact mass ofthe protein. The amino acid sequence of EDEN-1 was found tobe homologous to lectin ESA-2 from E. serra. This is the firstknown report of a cDNA sequence for this family of proteins.Consistent with its homology to lectin-like proteins, EDEN-1 ismainly beta-sheet based on its circular dichroism spectrum.EDEN-1 also shows weak glucoside hydrolase activity,suggesting that it may bind to carbohydrate moieties despite alack of appreciable hemagglutinating activity.
© 2026 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering