VOLUME 11 NUMBER 2 (July to December 2018)
Philipp. Sci. Lett. 2018 11 (2) 075-083
available online: November 09, 2018
*Corresponding author
Email Address: lcvillegas1@up.edu.ph
Date Received: August 04, 2018
Date Revised: October 22, 2018
Date Accepted: October 30, 2018
ARTICLE
Silver Nanoparticles Extracellularly Produced by Serratia sp. NBL1001 Have Antibacterial Properties
by Mary Faith Y. Adan1, Zyne K. Baybay2, Nacita B. Lantican1, Lilia M. Fernando2, Erlinda S. Paterno3, Lucille C. Villegas*1, Leodevico L. Ilag4, Andrew D. Montecillo1
1Microbiology Division, Institute of Biological Sciences, College of Arts and Sciences,
University of the Philippines Los Baños, Laguna 4031, Philippines
2Nanobiotechnology Laboratory, National Institute of Molecular Biology and
Biotechnology (BIOTECH), University of the Philippines Los Baños, College,
Laguna 4031, Philippines
3Division of Soil Science, Agricultural Systems Institute, College of Agriculture
and Food Science, University of the Philippines Los Baños, College,
Laguna 4031, Philippines
4Xerion Limited, 246 Esplanade, Brighton, Victoria 3186, Australia
University of the Philippines Los Baños, Laguna 4031, Philippines
2Nanobiotechnology Laboratory, National Institute of Molecular Biology and
Biotechnology (BIOTECH), University of the Philippines Los Baños, College,
Laguna 4031, Philippines
3Division of Soil Science, Agricultural Systems Institute, College of Agriculture
and Food Science, University of the Philippines Los Baños, College,
Laguna 4031, Philippines
4Xerion Limited, 246 Esplanade, Brighton, Victoria 3186, Australia
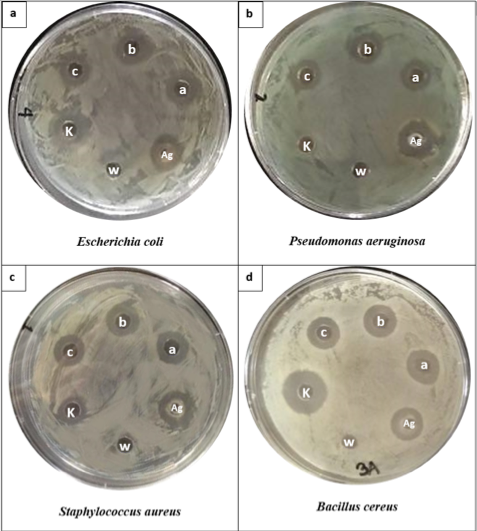
The emergence of multidrug resistant microorganisms ignited interest in silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) and their application as antimicrobial particles. In this study, the synthesis of AgNPs by a wildtype isolate, Serratia sp. NBL1001, and preliminary characterization and antibacterial activity of the produced AgNPs were investigated. Extracellular biosynthesis of AgNPs from silver nitrate (AgNO3) was observed by visual inspection of the crude cell-free NBL1001 supernatant, showing color changes from pale yellow to orange-brown. UV/Vis scanning spectroscopy of the AgNO3-NBL1001 supernatant solution, upon incubation overnight at 35°C, showed peaks at 430-440 nm, typical for AgNPs. Scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive x-ray confirmed the presence of AgNPs in the solution, with size range of 15.29-61.78 nm and mean size of 28.80 nm (n=30). Agar-well diffusion assay showed that the AgNPs exhibited antibacterial activity against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Bacillus cereus and Staphylococcus aureus. The mean value of the antimicrobial indices exhibited by the AgNPs was highest against B. cereus at 1.29, followed by those of E. coli at 1.19, then S. aureus at 1.10, and the least was that of the P. aeruginosa at 1.0. The results demonstrated that Serratia sp. NBL1001 conditioned media can mediate the extracellular synthesis of AgNPs with antibacterial activities against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
© 2024 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering