VOLUME 13 NUMBER 2 (July to December 2020)
Philipp. Sci. Lett. 2020 13 (2) 198-205
available online: December 22, 2020
*Corresponding author
Email Address: jfsimbahan@up.edu.ph
Date received: January 31, 2020
Date revised: May 12, 2020
Date accepted: November 30, 2020
ARTICLE
Marilao-Meycauayan-Obando River System (MMORS) Harbors Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria Indicating High Risk of Antimicrobial Contamination
Sarah Jean G. Supnet, Eloisa Victoria M. Caballero, Raymond H. Parcon, and Jessica F. Simbahan*
Institute of Biology, College of Science,
University of the Philippines Diliman,
Quezon City, Philippines
University of the Philippines Diliman,
Quezon City, Philippines
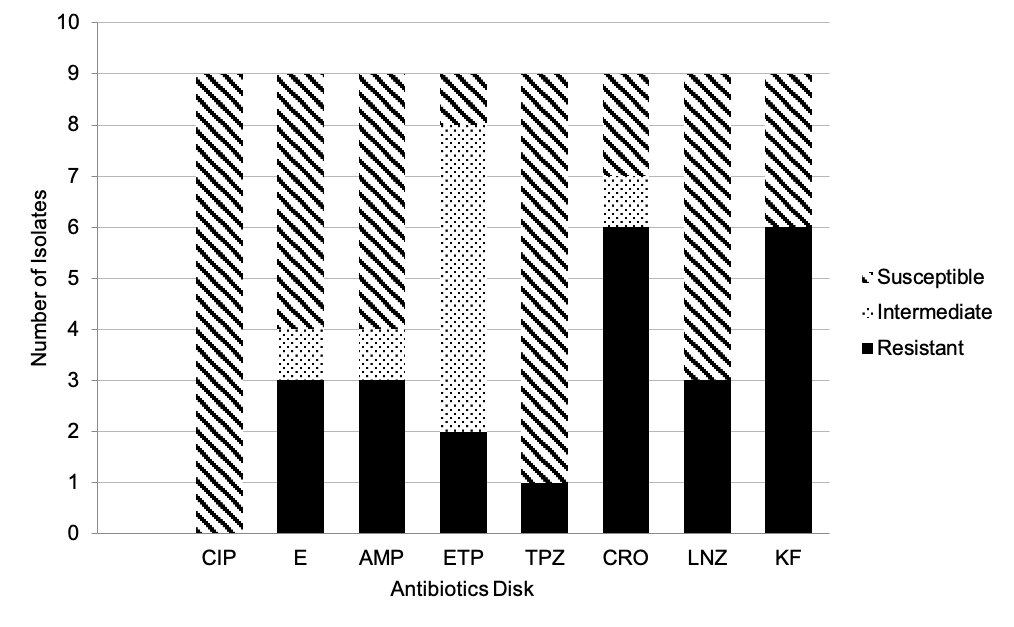
Marilao-Meycauayan-Obando River System (MMORS) is among the dirtiest and most polluted places in the world but it is still utilized for aquaculture, recreation, and water supply. Since it is contaminated with various industrial and commercial wastes, it is likely that effluents with antibiotics are also dumped into the river system. Antibiotic resistance is one of the biggest threats to global health, food security, and development. Nine (9) bacteria isolated from MMORS were screened for antibiotic resistance using eight (8) antibiotics of different classes, i.e., ciprofloxacin (5mcg), erythromycin (15mcg), ampicillin (25mcg), ertapenem (10mcg), ceftriaxone (30mcg), linezolid (30mcg), cephalothin (30mcg), and piperacillin/tazobactam (100/10mcg). MS1 and MS5 had the highest multiple antibiotic resistance (MAR) index at 0.625, followed by MS4, MS6, MS7, and MS8 at 0.375. MS2 and MS9 had MAR index of 0.125. The proportion of isolates with MAR index greater than 0.2 (66.66%) was higher than isolates with MAR index below 0.2 (33.33%), suggesting a high risk of contamination in sampling sites. Sequence analysis revealed that MS1 had 99.87% sequence similarity with Bacillus pumilus, MS2 with 99.30% Bacillus sp. sequence similarity, MS3 with 93.08% Brevibacillus sp. sequence similarity, MS4 with 99.90% Morganella morganii sequence similarity, MS5 with 100.00% Bacillus cereus sequence similarity, MS6 with 99.78% Escherichia coli sequence similarity, MS7 with 100.00% Bacillus anthracis sequence similarity, and MS9 with 100.00% Bacillus sp. sequence similarity. This study provides initial insight into multidrug-resistant bacteria and its possible risk in safety and public health in MMORS.
© 2026 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering