VOLUME 14 NUMBER 1 (January to June 2021)
Philipp. Sci. Lett. 2021 14 (1) 180-190
available online: June 30, 2021
*Corresponding author
Email Address: rrwengramos@gmail.com; rowena.ramos@fprdi.dost.gov.ph
Date received: October 06, 2020
Date revised: May 17, 2021
Date accepted: June 21, 2021
ARTICLE
Molecular Characterization of Pediococcus acidilactici Pediocin Genes (ped PA-1/AcH) and Plasmid Transfer into Bacillus subtilis NRRL B-3749 via Electroporation
Rowena E. Ramos*1, Francisco B. Elegado2, Maria Teresa M. Perez2, Noel G. Sabino3, and Antonio C. Laurena4
1Department of Science and Technology-
Forest Products Research and Development Institute,
Forestry Campus University of the Philippines
Los Banos Laguna Philippines 4031
2National Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology,
University of the Philippines Los Baños,
College Laguna Philippines 4031
3Institute of Biological Sciences, College of Arts and Science,
University of the Philippines Los Baños,
College Laguna Philippines
4Institute of Plant Breeding, Crop Science Cluster
University of the Philippines Los Baños,
College of Agriculture and Food Science,
University of the Philippines Los Baños,
College Laguna Philippines 4031
Forest Products Research and Development Institute,
Forestry Campus University of the Philippines
Los Banos Laguna Philippines 4031
2National Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology,
University of the Philippines Los Baños,
College Laguna Philippines 4031
3Institute of Biological Sciences, College of Arts and Science,
University of the Philippines Los Baños,
College Laguna Philippines
4Institute of Plant Breeding, Crop Science Cluster
University of the Philippines Los Baños,
College of Agriculture and Food Science,
University of the Philippines Los Baños,
College Laguna Philippines 4031
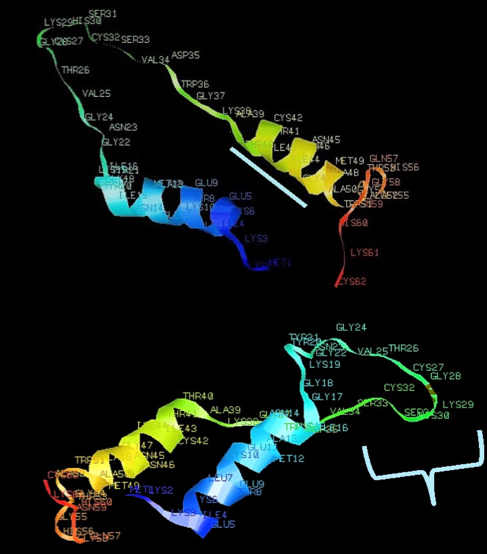
Crude pediocin preparations (Class IIa bacteriocin) of selected Pediococcus acidilactici strains S3, K2A2-3 and 3G3 inhibited the growth of Listeria innocua 026. The pap genes (papABC) of the pediocin operon were amplified from S3, K2A2-3 and 3G3 to further study the mechanism of pediocin production. Pediocin gene sequences were obtained for possible use in downstream and engineering activities. Primer designs for papB and papC gene amplification involved sequence alignments (CLC Sequence Viewer 7.6.1, BLASTn) and computational tools (SnapGene and AmplifX 1.6.1) via homologous sequences derived from the NCBI database. The pap gene amplicons were sequenced and protein structures predicted via available online tools such as ExPASY, Phyre2, and COFACTOR. Characterization via generated protein structures revealed the ligand-binding sites which reinforce possible functions of PedA, PedB, and PedC proteins on cell inhibition, immunity, and repair. Bacillus subtilis NRRL B-3749 competent cells served as the host for the transfer of the plasmid encoding the pediocin operon. The putative transformant B235 was found to be most inhibitory to Listeria innocua 026 better than the control strains in plate assays.
© 2024 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering