VOLUME 15 NUMBER 2 (July to December 2022)
SciEnggJ. 2022 15 (2) 128-144
available online: November 30, 2022
*Corresponding author
Email Address: jrcdizon@bpsu.edu.ph
Date received: September 04, 2022
Date revised: November 09, 2022
Date accepted: November 13, 2022
REVIEW
3D-Printed Polymeric Spare Parts for Industrial Applications: A State-of-the-Art Review
Ciara Catherine L. Gache1, Brian J. Tuazon2,3, Michaela T. Espino1,3, Rigoberto C. Advincula4, and John Ryan C. Dizon*1,3
1Department of Industrial Engineering,
College of Engineering and Architecture,
Bataan Peninsula State University-Main Campus, City of Balanga,
Bataan, 2100, Philippines
2Department of Mechanical Engineering,
College of Engineering and Architecture,
Bataan Peninsula State University-Main Campus, City of Balanga,
Bataan, 2100, Philippines
3DR3AM Center, Bataan Peninsula State University-Main Campus,
City of Balanga, Bataan, 2100, Philippines
4Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and
Institute for Advanced Materials and Manufacturing,
University of Tennessee,Knoxville, TN 37996, USA;
Department of Macromolecular Science and Engineering,
Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH 44106, USA;
Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996, USA;
Center for Nanophase Materials and Sciences,
Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37830, USA
College of Engineering and Architecture,
Bataan Peninsula State University-Main Campus, City of Balanga,
Bataan, 2100, Philippines
2Department of Mechanical Engineering,
College of Engineering and Architecture,
Bataan Peninsula State University-Main Campus, City of Balanga,
Bataan, 2100, Philippines
3DR3AM Center, Bataan Peninsula State University-Main Campus,
City of Balanga, Bataan, 2100, Philippines
4Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and
Institute for Advanced Materials and Manufacturing,
University of Tennessee,Knoxville, TN 37996, USA;
Department of Macromolecular Science and Engineering,
Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, OH 44106, USA;
Department of Materials Science and Engineering,
University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN 37996, USA;
Center for Nanophase Materials and Sciences,
Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN 37830, USA
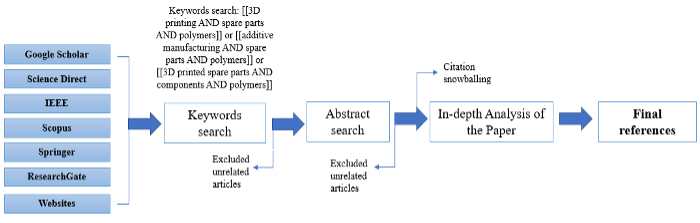
3D-printed polymers are already being widely used in different disciplines. Producing component and spare parts proves to be one of its more critical functions. This paper discusses 3D-printed polymeric component and spare parts in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, maritime, medical, and manufacturing, as well as the challenges being faced in the adoption of the 3D printing technology in these industries. The common 3D printing technologies and materials used to produce spare parts are summarized and briefly discussed. Lastly, the opportunities, challenges, and future outlook of using 3D printing in the production of spare parts are presented.
© 2024 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering