VOLUME 16 (Supplement)
SciEnggJ 16 (Supplement) 067-089
available online: October 20, 2023
*Corresponding author
Email Address: lsreyes@msi.upd.edu.ph
Date received: August 30, 2023
Date revised: September 18, 2023
Date accepted: September 19, 2023
DOI: https://doi.org/10.54645/MFFR36805
ARTICLE
Genomics and metabolomics-based assessment of the biosynthetic potential of the sponge-associated microorganism Streptomyces cacaoi strain R2A-843A from the Philippines
Marine Science Institute, College of Science,
University of the Philippines, Diliman, Quezon City, 1101, Philippines
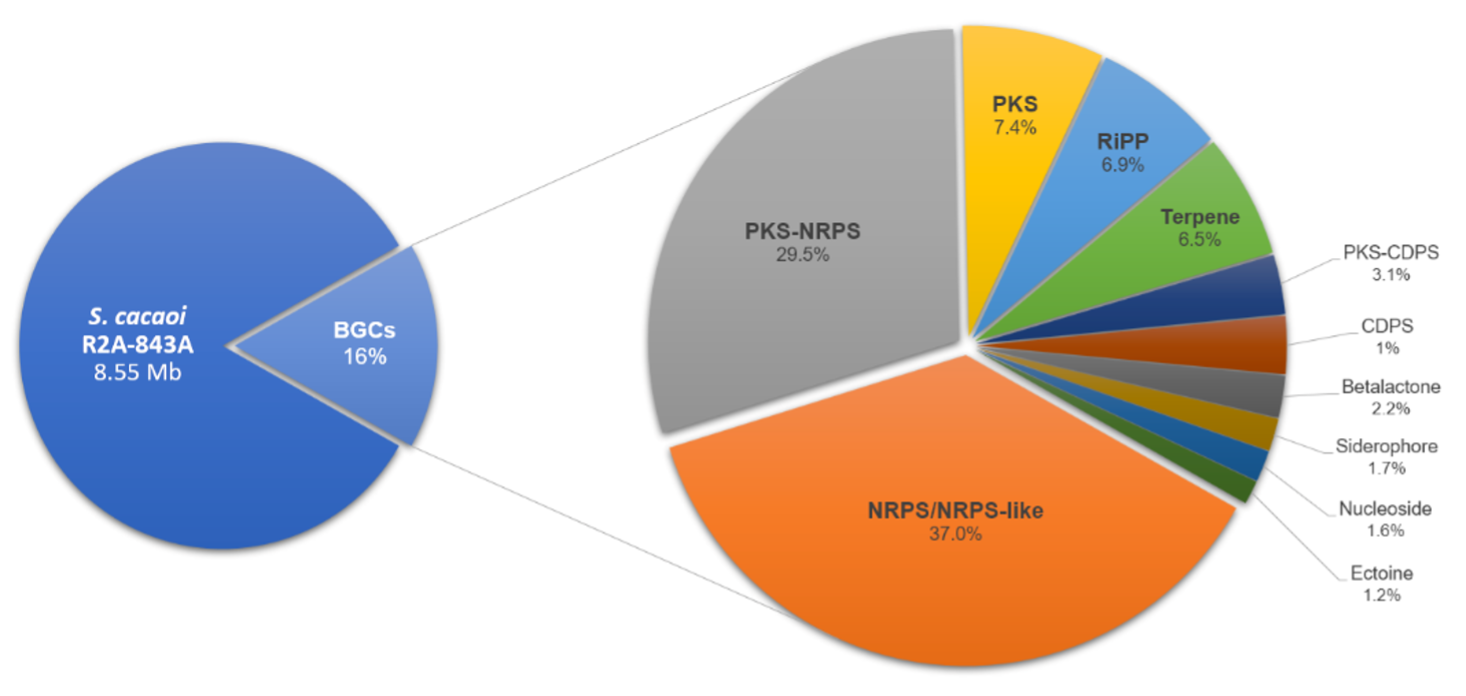
The biosynthetic machinery of the sponge-associated Streptomyces cacaoi strain R2A-843A was assessed using a combined genomics and metabolomics approach. Whole genome sequencing and molecular networking showed the high biosynthetic potential of this actinomycete. A significant proportion of the genome is dedicated to secondary metabolite production, with biosynthetic gene clusters for nonribosomal peptides, polyketides, and terpenes being the most represented. Seven cyclic pentapeptides, including a putative new analogue, and a glycosylated lanthipeptide were identified using HRMS and untargeted MS/MS analysis. To validate our genome and metabolome analysis, we undertook a mass spectrometry-guided purification and confirmed the production of the known peptides BE-18257A (1) and BE-18257B (2). The production of 1 and 2 and the growth of the microorganism were monitored for eight days. Compound 2 was produced at a higher concentration, starting at 48 h post-incubation. Both compounds were noncytotoxic against colorectal and breast cancer cell lines.
© 2026 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering