VOLUME 17 NUMBER 2 (July to December 2024)
SciEnggJ. 2024 17 (2) 168-174
available online: July 01, 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.54645/2024171DAL-61
*Corresponding author
Email Address: elmar.villota@clsu2.edu.ph
Date received: March 14, 2024
Date revised: May 27, 2024
Date accepted: May 27, 2024
ARTICLE
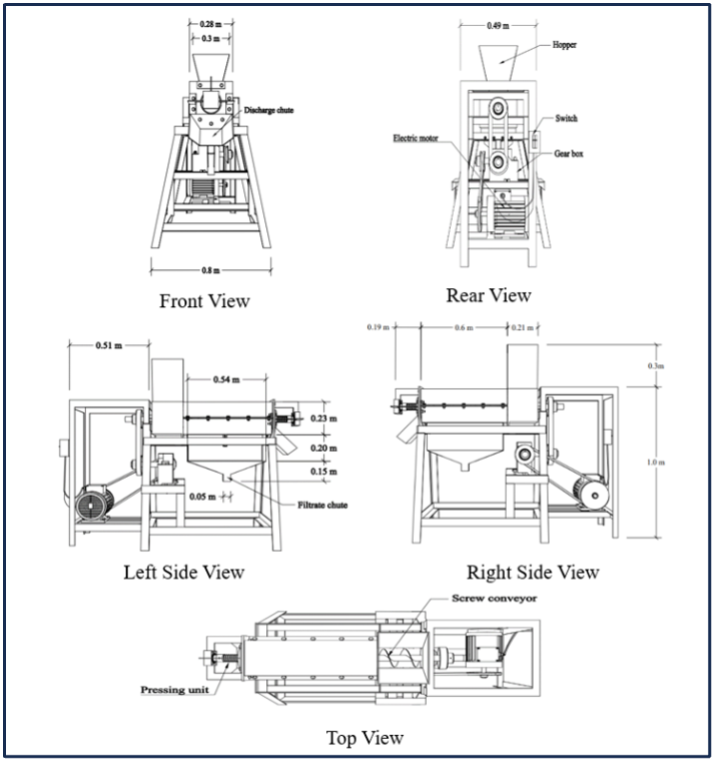
Design and fabrication of chicken manure dewatering machine
Nueva Ecija, Philippines
2Department of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering,
Central Luzon State University, Nueva Ecija, Philippines
Screw press conveyors are widely used in a wide range of industrial applications, particularly for managing substances such as pig slurry and cattle slurry (sludge). However, adapting a screw press conveyor to handle fresh chicken waste presents significant challenges. In the field of poultry farming, the development of a specific dewatering machine modified to chicken manure is critical. Our principal focus is on the development of such equipment, specifically designed to handle the high moisture content of chicken manure. Our primary goal is to effectively handle the daily waste output of a poultry house with 40,000 chickens. This study assesses the performance of a recently developed Chicken Manure Dewatering Machine by examining its capacity and effectiveness. We carefully assessed the machine's capabilities, utilizing experimental methods with three different treatments (17 rpm, 22 rpm, and 29 rpm). The results show significant actual capacities of 351.40 kg/h, 443.60 kg/h, and 619.40 kg/h, machine efficiency of 86.9%, 90.9% and 96.3%, and separation efficiencies of 17.2%, 13.1%, and 9.7%, respectively. These results confirm the machine's efficacy in efficiently dewatering chicken manure, making it a feasible solution for poultry waste management. The conclusion emphasizes the practical implications of these findings and advocates for further exploration and enhancement of sustainable agricultural practices.
© 2026 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering