VOLUME 17 (Supplement)
SciEnggJ 17 (Supplement) 356-361
available online: August 05, 2024
DOI: https://doi.org/10.54645/202417SupSOE-29
*Corresponding author
Email Address: dabban.rg.s@slmc-cm.edu.ph
Date received: 11 January 2024
Date revised: 10 July 2024
Date accepted: 29 July 2024
ARTICLE
MicroRNA-21, C-C chemokine receptor type 7, and twinfilin actin binding protein 1 expression in fresh frozen breast tissue samples
Medicine-WHQM, Quezon City, Philippines
2College of Medical Technology, Trinity University of Asia,
Quezon City, Philippines
3Human Cancer Biobank - Research and Biotechnology Group,
St. Luke's Medical Center, Quezon City, Philippines
4Department of Biology, De La Salle University, Manila City,
Philippines
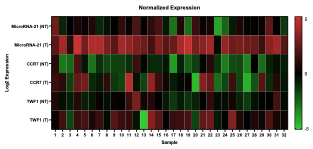
Breast cancer ranks second worldwide as the most common cancer in both sexes and is the leading cancer in women. Individuals at high risk of developing breast cancer are recommended mammography to detect early-stage disease. Although this technique was shown to reduce mortality, its usefulness is limited by high false-positive rates due to its inability to differentiate benign from malignant tumors. These problems highlight the need for markers to enhance breast cancer screening strategies. Proposed biomarkers, microRNA-21 (miRNA-21), C-C Chemokine Receptor Type 7 (CCR7), and Twinfilin Actin Binding Protein 1 (TWF1), were evaluated based on their role in cancer progression. In this retrospective analytical cross-sectional study, sixty-four fresh frozen breast tissue samples from the Human Cancer Biobank of St. Luke’s Medical Center Quezon City (i.e., 32 breast tumor samples with paired adjacent non-tumor tissue) were retrieved to evaluate the relative expression of miRNA-21, CCR7, and TWF1 using TaqMan® assays. MiRNA-16 was used for miRNA normalization, and 18S rRNA was used for gene expression normalization. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to examine the diagnostic capabilities of the studied biomarkers. MiRNA-21 (P<.001), CCR7 (P=.003), and TWF1 (P=.003) expression had a significant difference in breast tumors from the paired non-tumor tissue. Additionally, miRNA-21 and TWF1 were able to differentiate early-stage (P<.001; P=.008) and late-stage (P<.001; P=.009) breast tumors from non-tumors. In contrast, CCR7 only differentiated early-stage breast tumors (P=.014). No significant differences were observed between early and late-stage breast tumors. Furthermore, ROC curves of miRNA-21, CCR7, and TWF1 were all statistically significant with area under the curve values of 0.951, 0.697, and 0.733, respectively. MiRNA-21 testing offers to augment the current cancer diagnostic strategy if less invasive samples, such as whole blood, become the sample of choice for testing. However, larger cohorts are needed to validate the clinical implications of the studied biomarkers in breast cancer monitoring.
© 2026 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering