VOLUME 18 NUMBER 1 (January to June 2025)
SciEnggJ. 2025 18 (1) 001-010
available online: January 31, 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.54645/2025181PLI-41
*Corresponding author
Email Address: mbgalang1@up.edu.ph
Date received: April 30, 2024
Date revised: June 17, 2024
Date accepted: July 02, 2024
ARTICLE
Process optimization of flour from Philippine purple-fleshed sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. var. SG18-150-01) using Response Surface Methodology
and Food Science, University of the Philippines, Los Baños,
Laguna, Philippines
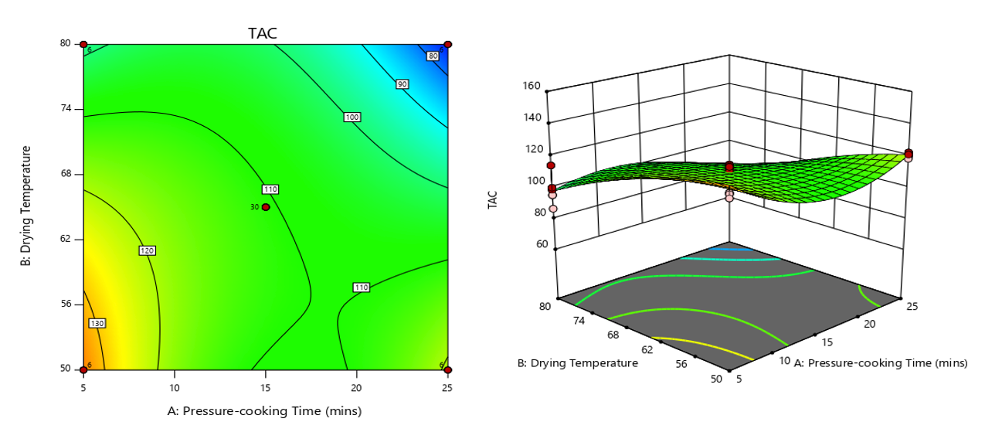
Processing purple-fleshed sweet potato (PFSP) into flour minimizes post-harvest losses as it has a longer shelf-life and can be used for various food product applications. The anthocyanins naturally occurring in PFSPs also provide promising color with added health benefits to consumers. However, the stability of this phytonutrient depends on several factors, thus optimizing the process of flour production is crucial. The study aimed to determine the optimum processing conditions of the purple-fleshed sweet potato flour (PFSPF) using the SG18-150-01 variety. Response Surface Methodology (RSM) was employed using a three-level factorial design following Central Composite Design to assess the effects of pressure-cooking time (5-25 minutes) and drying temperature (50-80°C) on the response variables. The generated optimum process is composed of a time-temperature combination of 5 minutes and 50.36°C which then resulted in a 143 mg cyanide-3-glucoside (c3g)/100g of anthocyanin content and 5.26 mg Trolox equivalents (TE)/g antioxidant activity. The model used to predict the response is found to be dependable as the actual values were close to the predicted. The optimized and stable PFSPF can be used as a functional ingredient, particularly in the baking industry.
© 2026 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering