VOLUME 18 NUMBER 1 (January to June 2025)
SciEnggJ. 2025 18 (1) 191-200
available online: 21 May 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.54645/2025181IBG-95
*Corresponding author
Email Address: dcsoriano@up.edu.ph
Date received: 05 July 2024
Dates revised: 16 October 2024
Date accepted: 15 May 2025
ARTICLE
The ecological quality of the Abra River watershed in Northern Luzon, Philippines using the remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) model
Gov. Pack Road, Baguio City, Philippines 2600
2Department of Geography and Environmental Science,
University of Reading, Reading, United Kingdom RG6 6A1
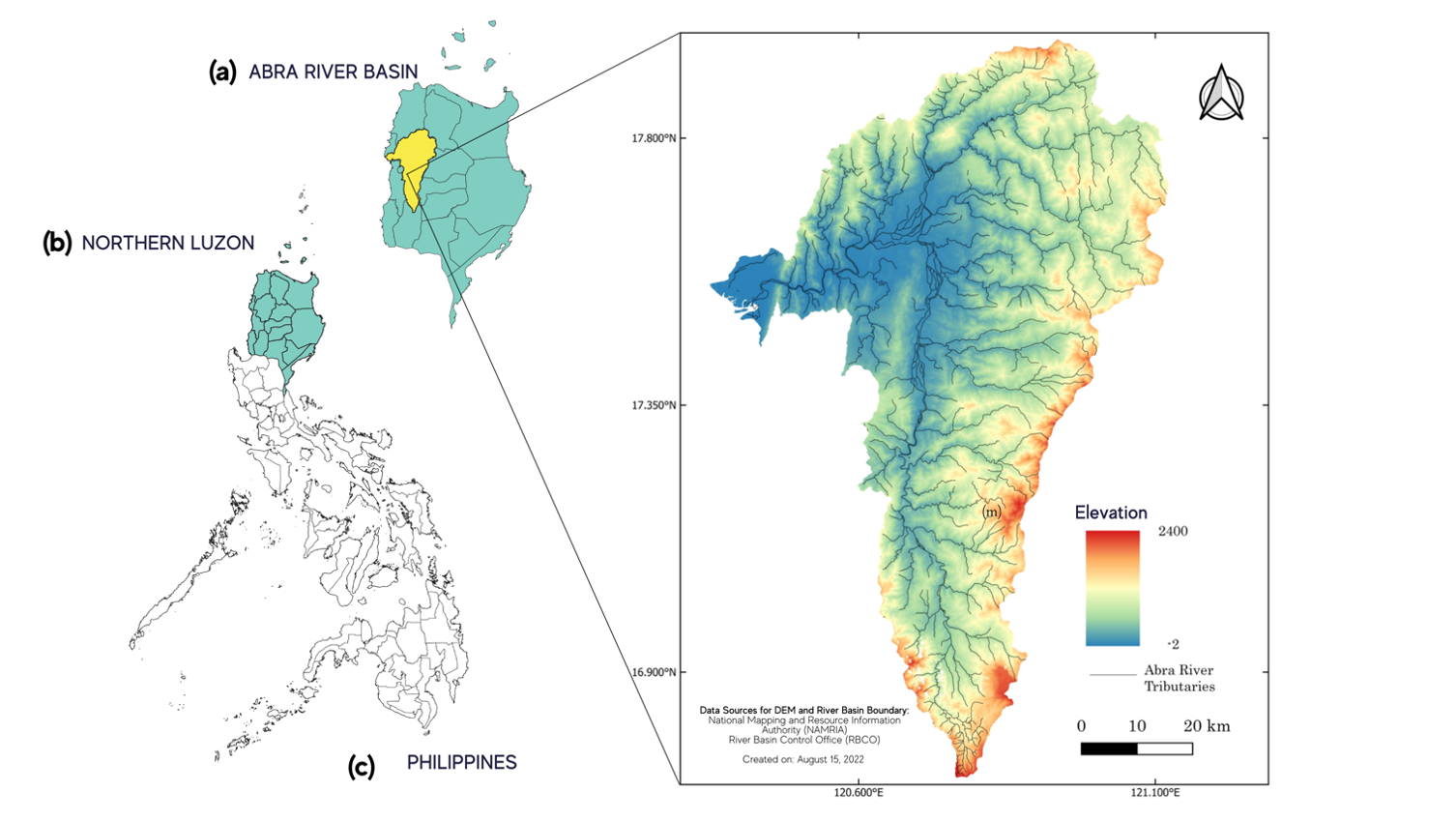
Ecological quality is an integral facet of the overall state of an ecosystem which relates to how the biotic and abiotic components interact within the environment and how these structure-process complexes translate to the delivery of an array of ecosystem services that support human welfare and development. Modern and useful methods have been devised to assess the ecological quality of largescale ecosystems such as rivers and watershed. Using remote sensing technology, the ecological status of ecosystems can be evaluated and monitored spatiotemporally. This study focuses on establishing the ecological quality of the Abra River ecosystem and its watershed in Northern Luzon, Philippines by analyzing remote sensing data over a two-year period (2020-2021), using the Remote Sensing Ecological Index (RSEI) model. A remote sensing ecological index (RSEI) was formulated using four various sub-indices: the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI), normalized differential build-up and bare soil index (NDBSI), land surface moisture (LSM), and land surface temperature (LST). The RSEI model was built and acquired using a principal component analysis (PCA) method to integrate the four sub-components. Results showed that the mean RSEI score for the study area is 0.60 (moderate to good) with the NDVI (0.641) and LSM having positive contributions to ecological quality while NDBSI (-0.674) and LST (-0.138) having negative weights to the ecosystem. This study is necessary as there are limited works on the ecological status of the Abra River basin and thus can contribute to responsive efforts to conserve, manage, and protect large-scale ecosystems.
© 2026 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering