VOLUME 18 NUMBER 2 (July to December 2025)
SciEnggJ. 2025 18 (2) 356-364
available online: 27 October 2025
DOI: https://doi.org/10.54645/2025182FAS-39
*Corresponding author
Email Address: kbgumaru@up.edu.ph
Date received: 11 February 2025
Date revised: 30 May 2025
Date accepted: 26 September 2025
ARTICLE
Bibliometric analysis of global research on single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with tuberculosis infection
Pedro Gil St., Ermita, Manila
2Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of the
Philippines Manila, Pedro Gil St., Ermita, Manila
3Department of Medical Microbiology, College of Public Health,
University of the Philippines Manila, Pedro Gil St., Ermita, Manila
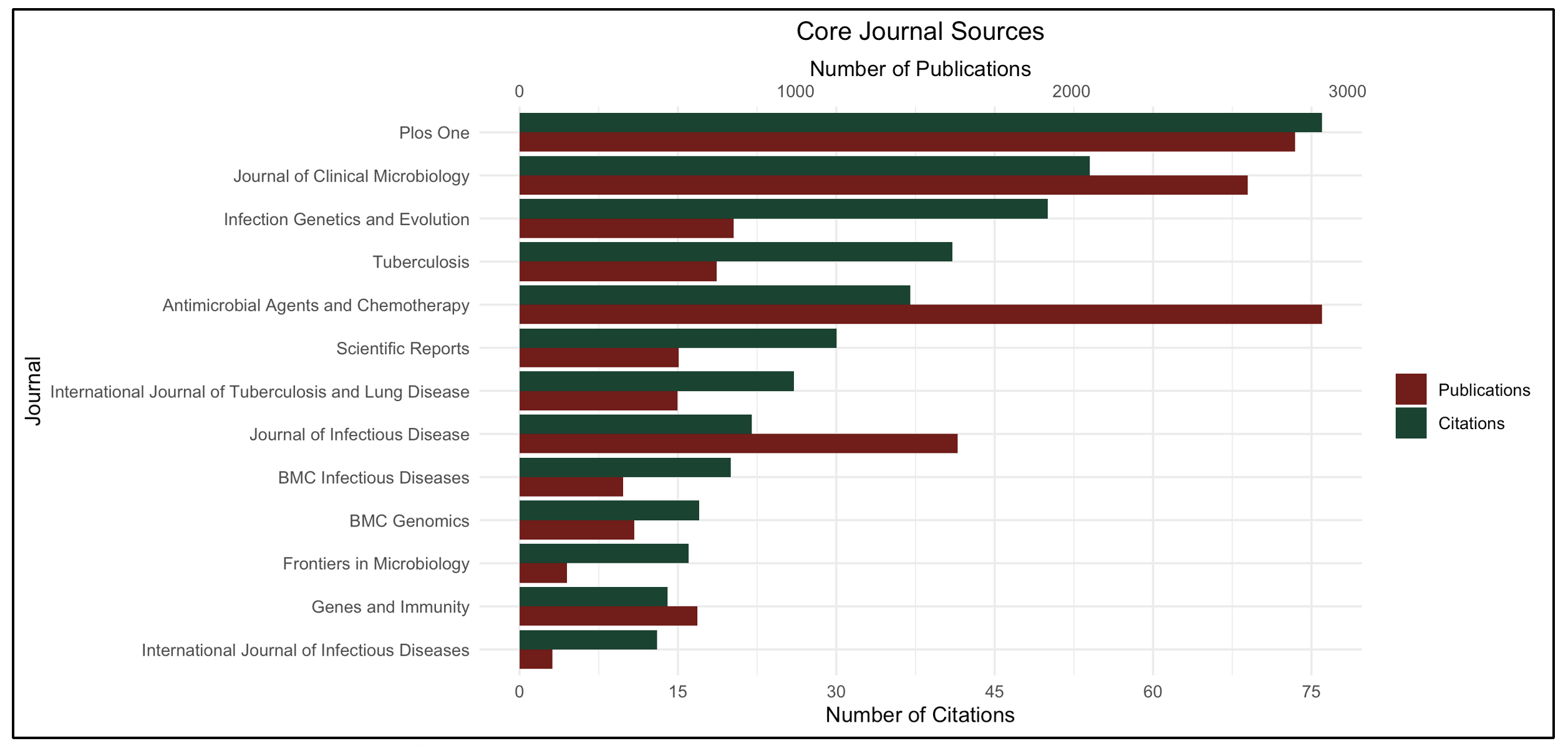
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious respiratory disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Around 25% of the world’s population is infected with M. tuberculosis, but only 5-10% develop TB infection. Genetic predispositions such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) contribute to the latency of TB infection in immunocompetent, infected individuals. This study provides an overview of the existing trends in global TB SNP research and the association of socioeconomic indicators with scientific productivity. A literature search for TB SNP research was conducted on SCOPUS articles published from 1992 to 2023. Bibliometrix was used to analyze all available bibliographic information. VOSViewer 1.6.20 was used for visualization in country and keyword analysis. Data on socioeconomic indicators were obtained from the World Bank. Correlation analysis was performed for socioeconomic indicators of countries and their scientific productivity indicated by total publications and citations. Research on TB SNP started in 1992, with 1,234 publications and 30,787 citations to date. Most are published in open-access journals. China has the most publications (338 publications), while the USA has the most citations (10,931 citations) and most collaborations (56 links). Immunology has been the focus of TB SNP research since 2010, but recent studies are exploring drug resistance. There is a significant association between scientific productivity and GDP, GDP per capita, international collaborations, R&D expenditure, and researchers in R&D. This study provided quantitative evidence for the current productivity, collaborations, and trends in TB SNP research. Administrators and policymakers can use the results to make evidence-based decisions about implementing TB-related health programs and research agenda.
© 2026 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering