VOLUME 19 (Supplement)
SciEnggJ 19 (Supplement) 009-014
available online: 09 January 2026
DOI: https://doi.org/10.54645/202619SupIKV-73
*Corresponding author
Email Address: nandiyanto@upi.edu
Date received: 10 September 2024
Dates revised: 28 January 2025
Date accepted: 02 January 2026
ARTICLE
Artificial intelligence, numerical simulation, and hybrid modeling in nanofluid heat transfer: A bibliometric and systematic decade review
2Semarak Ilmu Publishing, Kajang 43000, Malaysia
3Yayasan Bumi Publikasi Nusantara, Bandung 40154, Indonesia
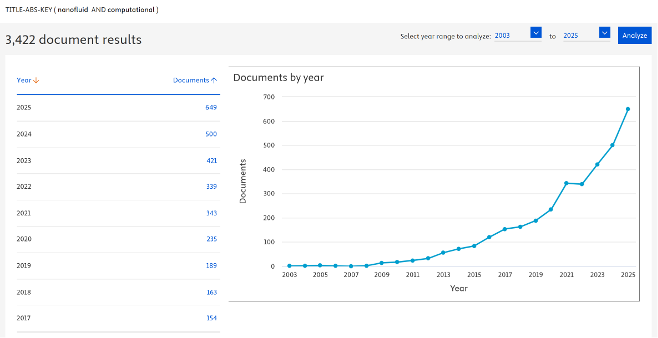
Recent advances in nanofluid heat-transfer research increasingly integrate computational fluid dynamics (CFD), artificial intelligence (AI), and hybrid modeling approaches to address complex, nonlinear transport phenomena. This study presents a systematic bibliometric and analytical review of nanofluid research combining numerical simulation and information technology (IT) over the past decade. Scopus-indexed publications from 2015 to 2024 were analyzed using bibliometric mapping to identify research trends, methodological evolution, and dominant modeling strategies. The results indicate a clear shift from standalone CFD-based analysis toward AI-assisted prediction and hybrid CFD-AI frameworks that balance physical fidelity and computational efficiency. Comparative assessment reveals that CFD remains essential for geometry-dependent and mechanistic analysis, AI enables rapid optimization and data-driven prediction, and hybrid approaches provide the most effective solution for complex multiphysics systems. Despite this progress, challenges persist in data availability, experimental validation, and modeling standardization. This study elevates bibliometric patterns into decision-oriented insights, providing practical guidance for selecting appropriate modeling strategies in nanofluid heat-transfer research and engineering applications.
© 2026 SciEnggJ
Philippine-American Academy of Science and Engineering